Is there really a bad effect of e-commerce on traditional brick and mortar businesses? Both sides have valid points to make, and compelling e-commerce statistics support them. We must first comprehend the history of e-commerce in order to make accurate forecasts about what the future holds for it and physical retailers.
A Brief History of E-Commerce
Even before the first web "browser" as we know it, e-commerce has a remarkably lengthy history. It has grown in tandem with other internet-based industries and emerged as a significant force in both offline and online trade. Thanks to e-commerce, creators and business owners from all over the world may now sell their products internationally.
The Initial Online Transaction
19 years prior to the creation of the first web browser, the first e-commerce transaction was carried out in 1971. It took place across a network between students organizing a sale at two universities, the Massachusetts Institute of Technology and the Stanford Artificial Intelligence Laboratory.
The Dotcom Boom
In 1992, two years after the World Wide Web browser was developed, the first commercial website as we know it today was established. But until 1995, when the US National Science Foundation relaxed its ban on commercial enterprise operations over the internet, e-commerce moved slowly. The first internet-only radio stations debuted in that year, along with the founding of both Amazon and eBay.
In 1999, just one year before the historic dotcom bust, global e-commerce hit $150 billion.
The Dotcom Bust
A period of quick, unrestrained growth in internet-based businesses came to an end in 2000 when the bubble burst. Investors started to fear when businesses started to fail just a few months after going public, causing the Nasdaq to decline by 78% from 2000 to 2002.
For some businesses and investors it was a catastrophe, but not for everyone. Companies who were strong enough to survive the crash started to merge and took over a bigger portion of the market.
The Dotcom Bust's Aftermath
Amazon and eBay are two examples of corporations that made it through the dotcom crisis and went on to rule the e-commerce sector. The bust was a significant setback, but the survivors saw it as a learning opportunity and continued.
These businesses quickly made a full recovery. PayPal was purchased by eBay in 2002 for $1.5 billion. Companies like Wayfair started to enter the market, selling goods through specialized domains focused at a small number of niche niches.
Alibaba, China's largest e-commerce company, saw a boom in the early 2000s, and China's unexpected rise in the digital market started to make headlines throughout the world.
Why Is E-Commerce Important, and How Vast Has It Grown?

One of the best e-commerce statistics that demonstrates the dominance of behemoths like Amazon is this: in 2015, Amazon alone was responsible for more than 50% of the growth in e-commerce. Nine percent of all retail sales over the previous year were accounted for by this growth in total. It is understandable why Amazon has become the preferred storefront for the vast majority of online retailers, fighting with one another to appear at the top of Amazon's search results, given the massive volume of e-commerce transactions that occur on their own.
Since that time, e-commerce has developed further, which has harmed traditional brick and mortar retail stores.
What developments in e-commerce are fueling the sector's expansion?
- Better Consumer Experience:
- Convenience:
- Customization Data:
- Customer Tracking:
A number of consumer-friendly improvements offered by e-commerce are quite appealing to some consumers. For instance, Amazon offers user reviews, which enable consumers to assess goods devoid of marketing influence. Users can utilize it as a method of crowdsourcing quality control by discussing what is and isn't worth their hard-earned money.
E-commerce also depends on the reality that consumers will frequently pay more for convenience, willingly paying shipping costs if it means they won't have to leave the comfort of their own house to buy goods.
The underlying strength of e-commerce is found in something that is a little more challenging to pin down to any one particular aspect. In addition to being convenient and personalized, it has a much wider audience than physical stores ever could. This has been made possible in part by advancements in data collection and analysis technology.
E-commerce can be tracked, and astute businesses take use of this to target their advertising and content to specific consumer groups.
Common Myths Regarding the E-commerce Sector
With all the excitement around e-commerce, it's simple to think that it will keep up with industry disruption and exponential growth. Though recall the dot com bust.
E-commerce is the subject of many misconceptions and myths, many of which can be harmful. Amazon didn't start making money until 2001, and since then, their profit margins have consistently lagged below those of the retail sector. However, the reason for their incredible success is volume.
Contrary to popular assumption, acquiring new customers in a digital market can be very expensive. Being recognised in the crowded field of digital advertising is incredibly challenging, especially on the biggest platforms like Facebook or Google.
Another widespread misconception is that only e-commerce companies can access the cutting-edge technologies that are boosting online sales. However, brick and mortar establishments can definitely benefit from the cutting-edge customer service and inventory management improvements made available to companies of all sizes by software services.
In the 1990s, relying on unfettered development was what caused so much hardship for investors and corporations. E-commerce is a crucial component of today's economy, but its development and management require careful and strategic consideration. It shouldn't be added to a sales strategy "simply because everybody else is doing it," as the saying goes.
Is traditional retail being destroyed by e-commerce?
The complicated answer is that there are a variety of both good and bad consequences of e-commerce on traditional brick and mortar retail. Similar to the dotcom boom, general e-commerce trends have caused a market correction that penalizes excessive expansion. Malls that have been abandoned, big-box store closures, and bankruptcies are indications of reckless growth.
Although e-commerce is one of the factors advancing this correction, brick and mortar stores are still thriving. The bland, uninspired, and change-resistant brands are dying thanks to the internet. The physical stores that are closing down were frequently already unprofitable.
Even while maintaining brick and mortar locations, firms that harness the technology that created e-commerce and comprehend why it is such a tremendous force can and will succeed.
E-commerce Future: Changes in Industry Trends and Growth

We know that e-commerce global sales are increasing, but if e-commerce isn't going to kill physical retail outlets, how will the industry evolve?
Individual makers, creators, and artists in the United States now have access to a much larger market to sell their wares through storefronts like Etsy. Amazon and Google are constantly improving their systems and introducing voice-first shopping technology, allowing users to make purchases without ever touching a screen. Monthly subscription "boxes" such as Dollar Shave Club, Blue Apron, and others are becoming extremely popular. What else is on the horizon?
Headless Commerce
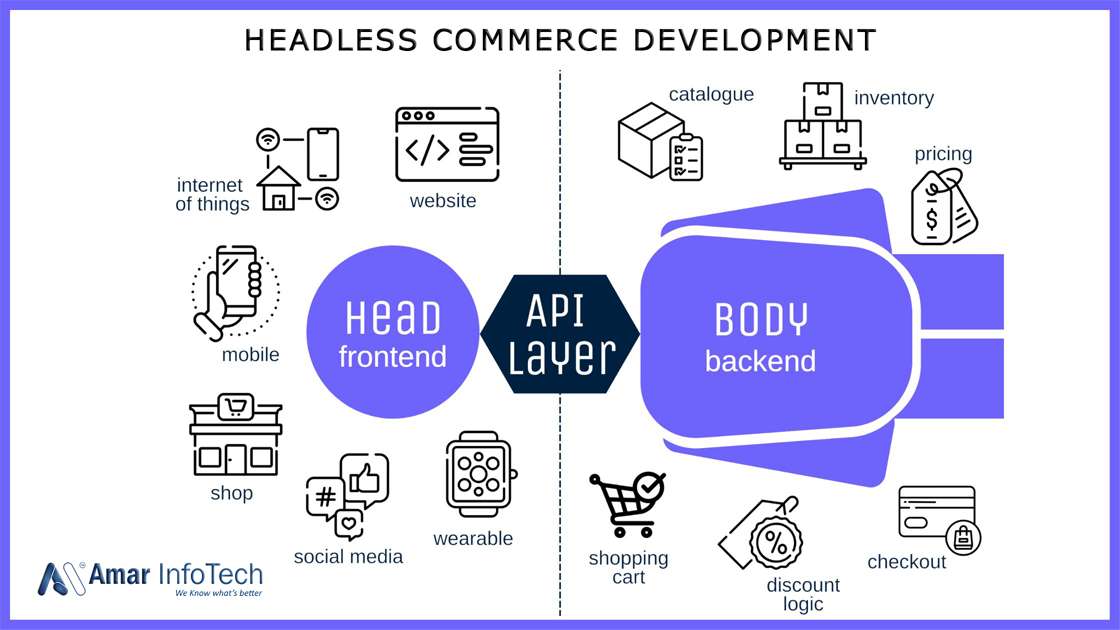
In its most basic form, headless commerce is the separation of an ecommerce application's frontend and backend. This architecture gives brands the freedom to build whatever and however they want. Above all, it enables brands to improve the customer experience.
The use of APIs, experience managers, and tools such as Heroku and Mulesoft, as well as the importance of IT partners, are all characteristics of headless. These resources are an essential component of any company's innovation strategy, delivering new functionality and experiences that engage customers and keep them ahead of expectations.
It's difficult to keep up with new touchpoints and experiences if you work in ecommerce, as you are probably aware of (and often requires a lot of coffee). In a traditional e-commerce model, new experiences may necessitate updates to both the front- and back-end systems, turning even minor projects into major headaches.
What are the benefits of headless commerce?
Adopters of headless commerce are typically larger enterprises with larger development and IT teams, as well as a do-it-yourself attitude. This makes sense, because the custom programming required to reliably produce and build a separate front end and back end can require a significant investment of development hours.
These companies frequently have months-long development queues and ambitious creative and marketing teams eager to test new designs, copy, and templates on the front end as soon as possible.
Following a pandemic that has shifted shopping to digital-first experiences, brands must embrace innovation as never before. Every hour of developer time is valuable, as speed-to-market is frequently linked to increased cash flow.
M-Commerce
Mobile commerce, also known as m-commerce, is the use of wireless handheld devices such as cellphones and tablets to conduct online commercial transactions such as product purchase and sale, online banking, and bill payment.
The use of mobile commerce is increasing. According to Statista, mobile commerce sales in the USA are expected to reach $431 billion by 2022.
Understanding Mobile Commerce
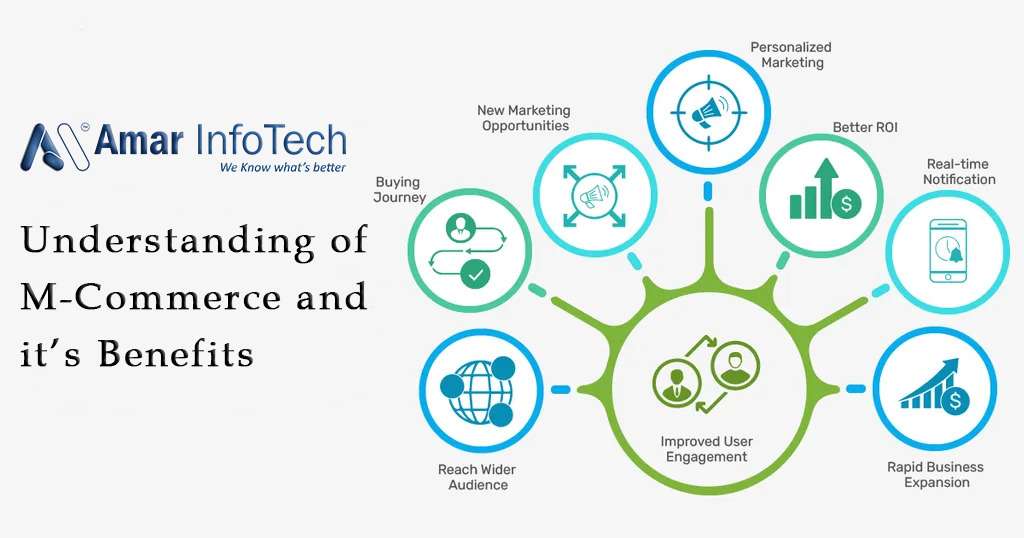
Mobile commerce is a growing subset of electronic commerce, a business model in which firms or individuals conduct transactions over the internet. According to the Pew Research Center, nearly 97% of Americans own a cell phone, and 85% own a smartphone, up from 35% in 2011.
M-commerce allows for the purchase of a wide range of products and services, including banking, investing, and the purchase of books, plane tickets, and digital music. Several factors have contributed to the rapid growth of mobile commerce, including increased wireless handheld device computing power, the proliferation of m-commerce applications, and the broad resolution of security issues.
Benefits of Mobile Commerce
The number of mobile commerce-capable devices is expanding. Customers can use digital wallets such as Apple Pay and Google Pay to make in-store purchases without having to swipe cards. In the mid- to late-2010s, social media platforms such as Meta (formerly Facebook), Twitter, Pinterest, and Instagram introduced "buy buttons" on their mobile platforms, allowing users to make purchases from other retailers directly from these social media sites.
Mobile device portability enables businesses to reach out to their customers via mobile commerce. Customers can receive coupons and discounts from retailers. Personalized shopping experiences can also help retailers connect with their customers.
M-commerce applications support GPS location monitoring to assist customers in finding things in their stores. M-commerce apps can further increase security because they support multi-factor authentication, which includes biometrics like fingerprint and retina scan identification.
Even though m-commerce has several advantages for both customers and businesses, most Americans still prefer to shop online. While 77% of American adults own a computer, just 15% of them use their smartphone as their only means of internet access, indicating that they have a broadband or cable service provider.
Q-Commerce
Q-commerce is flourishing, with businesses like Blinkit, Jokr, Weezy, Getir, and Flink springing up quickly all around the world. This development is definitely affected by Covid-19 lockdowns and the restricted access to necessities and home goods.
Q-Commerce meaning
Q-commerce, also known as "quick commerce," is a new, quicker version of e-commerce and is frequently used interchangeably with "on-demand delivery" and "e-grocery." It brings together the advantages of conventional e-commerce and advancements in last-mile delivery.
The only difference is in the delivery time, with the basic premise being the same. For delivery to be competitive, it must take 30 minutes or less rather than days.
As a result, people may now order a wider variety of items, with perishables like groceries filling a sizable market niche for q-commerce businesses. It frequently focuses on the micro, or on smaller amounts of fewer products. For instance, a recipe that is already underway that urgently needs a missing ingredient
"Consumers desire and anticipate having more things delivered to their doorstep than ever... There is no longer a 24- to 48-hour delivery wait time. Instead, a few minutes are now anticipated for this."
The larger, less obvious change occurs in the way q-commerce functions behind the scenes.
Every company operates differently, but many rely on "dark stores," which are strategically placed warehouses, to deliver orders quickly to customers' doorsteps. These typically contain more than 1,000 unique products and can range in size from 3229 to 7500 square feet (300 to 700 square meters).
Many also use crowdsourced labor, giving businesses access to a pool of people who are prepared to take action at any time.
These elements work along with others (such as the use of the most recent software and the design of dark stores themselves) to provide them the utmost agility and flexibility needed to skillfully respond to client demand around-the-clock.
What are the benefits of Quick Commerce?

Q-commerce distinguishes itself from conventional stores in 4 ways, according to customers:
- Speed
- Guaranteed availability of curated, relevant products
- 24 hour operation
- Ease
Companies that engage in q-commerce are able to deliver goods to customers faster than traditional retail establishments.
This is because of the previously mentioned hyper-local micro-fulfillment facilities (also known as "dark stores"), which are dispersed throughout highly populated areas of cities and placed close to those placing orders—typically no more than 3 km away. Accordingly, orders can be filled 25% quicker than they could with traditional in-store fulfillment.
Dark establishments don't have to give up valuable square footage to accommodate customers wandering aisles because every inch of their floor plan has been optimized for efficiency. Once orders are prepared, couriers can quickly travel between dark stores and clients' locations.
Due to investments in artificial intelligence and other technology that track demand and alter inventory in real-time, there is a higher likelihood that things will be accessible as well as quicker delivery. Intelligent software may identify trends in demand, and corporations can then ensure that goods are delivered in accordance with such patterns.
Additionally, they leverage mobile technologies to keep their army of couriers, who serve as the brand's face and play a crucial role, informed, skilled-up, and delivering superior customer care.
Dark stores are not constrained by specific daily opening hours like physical and mortar merchants are; they can operate 24 hours a day, 365 days a year.
This round-the-clock accessibility fits with the "always-on" lifestyle that smartphone technology has created, where individuals are up at all hours and have their phones close at hand.
Which would you choose if you had the option of continuing where you are, opening an app, and pressing a few buttons instead of stopping what you're doing, looking around for keys and cards, tying laces, walking a few blocks, then around the store in search of your items, being unable to find them so asking a staff member for help, queuing, paying, bagging items, and walking back home.
International Trends and Predictions in E-Commerce
However, China is a major player in the e-commerce sector and Alibaba, which provides its own e-commerce platform, is far larger than Amazon. To acquire a better understanding of the future of e-commerce, it is a good idea to look at the developments and experimentation in China. It would be foolish to ignore China given their swiftly expanding economy and the influence its tech firms have on international markets.
One example is that e-commerce systems are being tailored to fit smaller brick and mortar businesses, allowing mom-and-pop stores to use all the technology and power behind those platforms in exchange for a monthly subscription fee. Small firms who lack the resources to compete on their own in the digital market might use this outsourcing of retail logistics as a valuable strategy.
China has also gone beyond even same-day delivery; in some areas, they are processing orders and delivering groceries and food to customers' doors in less than 30 minutes. Infrastructure is needed to support this level of speed and ease, including warehouses, sophisticated inventory management systems, and other fast delivery options. Chinese tech giants are launching these things, and their technology may be used as the foundation for or even the source of these solutions in other regions of the world.
E-commerce Sustainability
Sustainability is one of the key issues at the forefront of e-commerce. Although customers now are increasingly likely to choose companies that uphold moral and ethical standards, supply chains continue to be major generators of waste and greenhouse gasses.
E-commerce companies can still contribute. There are several ways to cut waste in your supply chain, and doing so will also help you save money. All parties involved can benefit from the implementation of a lean supply chain by using cutting-edge data collection and analysis technologies.
Automation in E-commerce
Similar to other industries, the e-commerce sector has quietly advanced the automation of more logistics and fulfillment procedures while still being extremely visible in consumer-facing roles. Amazon's work on self-driving delivery vehicles and autonomous delivery drones is involved in many of the most well-known tests with e-commerce fulfillment automation. These drones and driverless cars will be sent out from warehouses to deliver goods right to customers' doorsteps.
There are less well-known locations where automation is still crucial and, unlike self-driving vehicles, is already in use. Chatbot-based automated customer support is becoming more effective and efficient, and it is evolving to be able to handle a wide range of consumer inquiries.
The widespread adoption of automated social media management systems and other marketing suites is a sign of the growing popularity of automated marketing and outreach platforms. Another crucial component of e-commerce is automated fraud detection, where payment information is saved to account credentials and continuously checked for fraud.
In brick and mortar retailers, grocery stores, and even restaurants, automated purchasing is becoming more prevalent. This enables customers to order and pay for goods without ever having to go to a register. Some Chinese furniture businesses are currently experimenting with virtual and augmented reality to enable customers see how things might appear and fit in their homes, creating a completely self-directed experience even inside the store, automated from the moment they walk in, to the moment they walk out.
Guide to Successfully Creating an Ecommerce Mobile App
The COVID 19 epidemic has significantly increased online buying and selling. Many stores are developing ecommerce mobile apps to produce significant revenue and satisfy the needs of local customers in order to maintain the change.
The development of Streamline Your Ecommerce Business Processes made it incredibly simple for new enterprises to launch an online store. We are aware that hiring a website developer may come to mind when you hear the words "creating an online store."
If we told you that you don't need any coding knowledge or technological background, would you believe us? You did hear correctly. We are here to make the difficult process of building apps, which is a barrier for the majority of online store owners. Due to a lack of internet understanding, many business owners even delay opening their online store.
This blog is devoted to new business owners who are interested in learning how to build an amazing online store.
You must first select an ecommerce software before you can launch an online store. We will walk you through the process of choosing the finest platform by weighing the advantages and features that are a must-have.
How Do You Choose the Best E-Commerce Platform for Your Online Store?

- Mobile friendly & Supports Mobile Apps
- Suitable for all Business Models
- Easy Customer Login Options
- User Friendly CMS
- Multiple Payment Options
- Integrated Shipping Options
- Attractive Themes
- Social Media Integration
Mobile commerce will surpass $600 billion in users by 2020. It is obvious that making an e-commerce website mobile-friendly is essential. If an e-commerce platform provides technical assistance for developing mobile websites, it is ideal. One company that offers full technical support when developing apps and mobile-friendly websites is Amar Infotech.
Do you prefer selling to consumers or businesses, or both? If both, your chosen platform must enable you to manage several business verticals simultaneously and in one location.
Your full e-commerce software must offer 4-5 login alternatives in order to ensure the success of the login process. Sign up, for instance, using your email, Facebook account, or Google+ account.
The term "CMS" stands for content management system, which enables owners of e-commerce websites to quickly generate, amend, and publish material throughout the entire website. Only the CMS makes it possible to alter your product pages or add new ones.
To provide clients more options when making payments, your full e-commerce platform should offer a variety of payment channels. It lessens the likelihood of cart abandonment owing to the unavailability of the desired payment method.
Adding a cheap delivery option to your e-commerce Apps might improve customer confidence. You can plan pickups, handle shipments immediately, and keep track of upcoming shipments.
The main goal while building an e-commerce app should be to have a visually appealing theme. If you have a compelling theme, you may win over clients quickly and perhaps convince them to make a purchase.
Customers have the option to post product reviews and images of recent purchases made directly from the retailer by using social sharing icons on apps. It serves as a marketing tool that motivates clients to spread the news about the business.
How to build e-commerce Apps in a few easy steps?
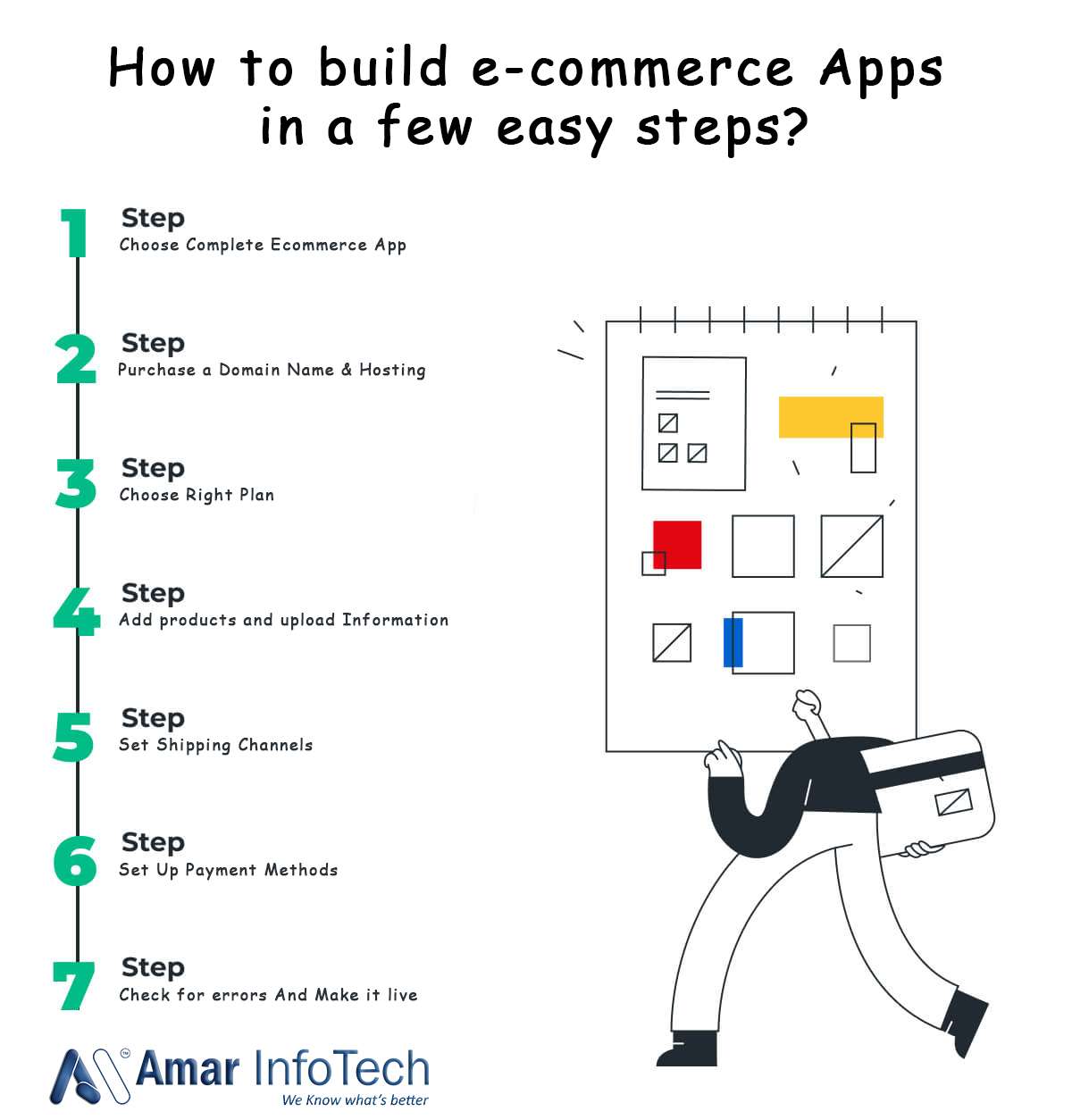
- Choose Complete Ecommerce App
- Purchase a Domain Name & Hosting
- Choose Right Plan
- Add products and upload Information
- Set Shipping Channels
- Set Up Payment Methods
- Check for errors And Make it live
The ideal apps must include a complete set of built-in functions to conduct daily operations with ease. If you decide to pursue development, share your present needs with us, and we'll give you the ideal solution for your company.
The following step is to purchase a domain name, an SSL, and web hosting. Your e-commerce apps are known by their domain names. Make sure it is original. Your apps' online home is like a web hosting service. Additionally, you will receive SSL while building an online store with Amar Infotech, which other softwares gives at an additional cost.
The following stage in building an e-commerce website is choosing a strategy that supports your business model. Different programmes from Amar Infotech are available to fit every budget and company need. Regardless of whether you want to sell B2C or B2B products or build a marketplace (like Amazon).
Making product pages is the next step in finishing ecommerce apps. You may show a 360-degree perspective of your products using our e-commerce platform's images, videos, and swatches. Pages must contain a lot of information. Mention the product's description, cost, pictures, offers, testimonials, and FAQs. Featured buttons like ADD TO CART and BUY NOW should be added. Product pages are prepared for publication.
Establish a shipping route that will assist in getting your orders delivered. Amar Infotech provides comprehensive integrated logistics solutions at low prices. Additionally, you can include any particular custom logistics partners.
Amar Infotech recommends using 2 integrated payment gateways by default. Depending on your location and the preferences of other users, you can select any one or more channels.
When everything is ready, run a test on your apps to check for internal errors. Once tested, make your app live and submit it for indexing on search engines (Google, Bing).
This is a straightforward approach for opening an online store with Amar Infotech. You can easily make high converting ecommerce apps by using the Amar Infotech entire ecommerce software guide. Additionally, it contains a database of numerous customizable themes that make it easier to develop an ecommerce software that meets your needs.
It makes use of PWA (Progressive Web Apps) stores technology to improve the mobile shopper experience. PWA indirectly contributes to speedier purchases in addition to building quick loading mobile websites.
Consider launching an online marketplace. We acted upon what you mentioned. Using the ecommerce software developed by Amar Infotech, you may create shopping stores with multiple vendors.
Final Words
As simple as using a smartphone is creating an app. To establish your store, you simply need to adhere to the proper procedures and pick an all-inclusive ecommerce solution.
It can be beneficial to do some research before purchasing an ecommerce website builder. Do your homework correctly, then. It is best to choose a platform by using the advice above.